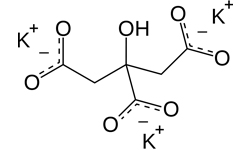
Potassium Citrate
|
SL. NO
|
TESTS
|
STANDARDS
|
||
|
1
|
Characters
|
|||
|
A
|
Description |
White, granular crystals or a crystalline powder; odourless;
hygroscopic. |
||
|
B
|
Solubility |
Very soluble in water; soluble in glycerin; practically
insoluble in ethanol (95%). |
||
|
2
|
Identification
|
|||
|
A
|
Reaction of Potassium salts | |||
|
i
|
Reaction A
|
A yellow or orange-yellow precipitate should be formed
immediately. |
||
|
ii
|
Reaction B
|
A white, crystalline precipitate should be formed.
|
||
|
iii
|
Reaction C
|
A yellow, crystalline precipitate should be formed which
on ignition should leave a residue of potassium chloride and platinum. |
||
|
B
|
Reaction of Citrates | |||
|
i
|
Reaction A
|
A white precipitate should be formed which should be
soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
||
|
ii
|
Reaction B
|
A violet colour should be produced which should change
to violet-blue. |
||
|
3
|
Appearance of Solution
|
Solution should be Clear and Colourless
|
||
|
4
|
Acidity or Alkalinity
|
Not more than 0.2 ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid or 0.1M sodium hydroxide should be required. |
||
|
5
|
Arsenic
|
Not more than 2 ppm.
|
||
|
6
|
Heavy Metals
|
Not more than 10 ppm.
|
||
|
7
|
Sodium
|
Not more than 0.3%
|
||
|
8
|
Chloride
|
Not more than 100 ppm.
|
||
|
9
|
Oxalate
(as anhy. oxalic acid) |
Not more than 300 ppm.
|
||
|
10
|
Sulphate
|
Not more than 150 ppm.
|
||
|
11
|
Readily Carbonisable Substances
|
The solution should not be more intensely coloured than
reference solution YS2 or GYS2. |
||
|
12
|
Water
|
Between 4.0% and 7.0%
|
||
|
13
|
Assay
|
Between 99.0% and 101.0%
|
||